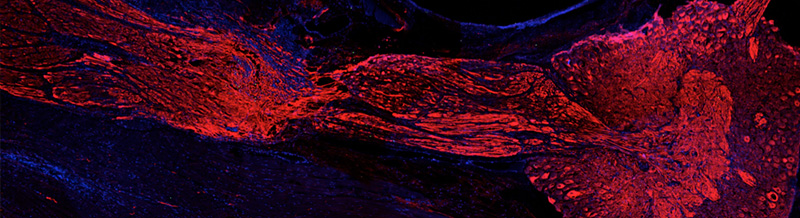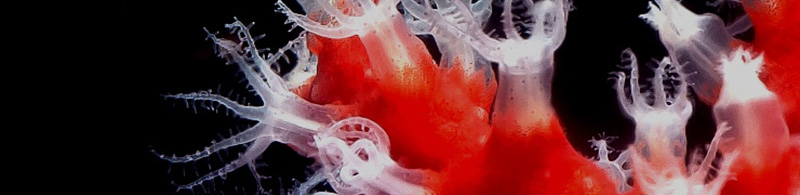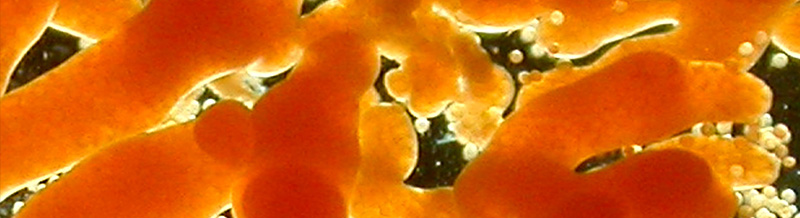
Animal evolution from a cell type perspective: multidisciplinary training in single-cell genomics, evo-devo and in science outreach
Summary
The aim of EvoCELL is to lay the foundation for a new branch of evo-devo focussing on cell types. We will study fundamental questions in animal evolution and development - eg. how new cell types arise in evolution, how many are in common between different animal groups and how many unique cell types have evolved in different animal lineages- using a new technology, single cell sequencing, which we will for the first time employ outside of lab models to sample the great diversity of animal phyla. EvoCELL will train a new generation of multidisciplinary scientists skilled in exploring the vast breadth of animal differentiation. We will jointly sample data from all major animal lineages, richly represented in the biodiversity of European waters, and develop new tools for comparative analyses, through which we will together pioneer three branches of cell evo-devo: evolution of stem cells; emergence of animal life cycles, and the stunning diversity of neural cell types. Through their excellent interdisciplinary and intersectoral training, from single-cell biology and palaeontology to bioinformatics and public outreach, our graduates will be in prime positions to assume leadership roles in academia, industry, and science outreach.
What we do
We are one of ten partners and are contributing to the diversity and evolution of neuronal cell types.
Partners
European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg - DE; Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, Napoli – IT; Uppsala University, Uppsala – SE; University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg – DE; University of Exeter, Exeter - UK; University College London, London – UK; Sars International Center for Marine Molecular Biology, Bergen – NO; Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Villefranches sur mer, Lion - FR; Non-academic partners: Museum für Naturkunde, Berlin – DE; Genomix4Life, Salerno - IT
Research Area
Organismal Biology
Project Lifetime
January 2018 to December 2022
SZN Role
Partner
Principal Investigator
People involved
2 ESRs to be hired
Funding Institution
European Commission, Horizon 2020 Call for Proposal: H2020-MSCA-ITN-2017. Grant Agrement no. 766053.
Contribution to SZN
€344081,76 (EU contribution)
Dedicated website
Media - Pictures

Meet the team
Maria I. Arnone, Researcher
Periklis Paganos, PhD student
Coordinated Research Infrastructures Building Enduring Life-science Services
Summary
CORBEL is an initiative of thirteen new biological and medical research infrastructures (BMS RIs), which together will create a platform for harmonised user access to biological and medical technologies, biological samples and data services required by cutting-edge biomedical research. CORBEL will boost the efficiency, productivity and impact of European biomedical research. Individually, the services offered by the BMS RIs are critical to their own user communities. Collectively, through CORBEL, they will be transformative across the range of life-science disciplines: from generation of knowledge at the bench to patient treatment at the bedside.
What we do
The SZN participate to the WP4 (Community Driven Cross-Infrastructure joint research – Bioscience): Use case 4 (Marine Metazoan Developmental Models for BioMedical research - from predictive integrated databases to functional testing), coordinated by CNRS-Villefrances-sur-Mer (Evelyn Houliston). Within this WP the SZN hired for 18 mo the bioinformatician postdoc Elijah K. Lowe to work at enabling genomics and databases for Paracentrotus lividus.
Partners
Altogether, the CORBEL consortium comprises 37 individual partner institutions from 13 ESFRI Biological and Medical Sciences Research Infrastructures (BMS RI). Partners within WP4 are: EMBL-HD, EMBL-EBI, UMCU, ICFO, CRG, BRFAA, HMGU, CIRMMP, CSIC, CNRS, SZN, USTAN, FVB, MDC, VU/VUmc, DKFZ.
Research Area
Research Infrastructure
Project Lifetime
September 2015 to August 2019
SZN Role
Partner
Principal Investigator
People involved
Elijah K. Lowe - Salvatore D’Aniello - Anna Palumbo - Filomena Ristoratore
Funding Institution
European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme. Grant agreement No 654248.
Contribution to SZN
€90.700,00. (EU contribution)
Dedicated website
http://www.corbel-project.eu/home.html
Media - Pictures
 |
Migrazioni di mare: natura e cultura Martedì 11 dicembre 2018, ore 17.00 Introduce: Ulisse Cardini |
 |
Pensiero umano e intelligenza artificiale: relazioni pericolose? Martedì 6 novembre 2018, ore 17.00 Introduce: Maurizio Ribera d’Alcalà |
 |
Squali e miti: i mostri del Mediterraneo? Martedì 10 luglio ore 17.00 Sono intevenuti: Angelo Mojetta, Fabrizio Serena e Lorenzo Rossi |
 |
LA RICERCA E L'ITALIA: un rapporto difficile? Martedì 8 maggio ore 17.00 Introduce: Roberto Di Lauro Sono intervenuti: Roberto Defez, Andrea Graziosi, Tullio Jappelli, Roberto Di Lauro |
 |
Così vicini così lontani – l’uomo e gli altri Martedì 20 febbraio ore 17.00 Sono intervenuti: Emiliano Bruner, Elisabetta Visalberghi, Giancarlo Schirru |
 |
Presentazione del libro “Della Vecchiaia ovvero il posto delle fragole” di Domenico MazzulloMartedì 23 gennaio ore 17.00 |
Summary
ASSEMBLE Plus is a consortium of marine biological research stations in 16 countries, operating under the umbrella of the European Marine Biological Resource Centre (EMBRC-ERIC). The consortium provides scientists from academia, industry and government with transnational access to its marine biological research facilities, its historical data, and to advanced training opportunities, ASSEMBLE Plus aims to stimulate fundamental and applied research excellence in marine biology and ecology in Europe.
What we do
The 39 partner stations in the consortium provide access to a wide range of marine ecosystems, including the Red Sea, the Caribbean and Svalbard. We aim at attracting not only marine biological projects but also ones from non-marine sciences and from the private sector. We further aim to improve service provision by developing novel technologies and data solutions. Access to our stations is Trans-National, meaning that you can access ASSEMBLE Plus stations in any partner country other than the country in which you are employed.
If you wish to make use of this access program, you need to submit a short research proposal, and if this is selected, you will be able to carry out your proposed research at a marine partner station of your choice. The expenses of your stay as well as your travel costs will be covered, within certain limits, by ASSEMBLE Plus. If you are employed outside the EU, you can make use of the access program as well, but some restrictions apply.
For more information on ASSEMBLE Plus, including information on calls for proposals, rules, application- and access procedures, and submission deadlines, see http://www.assembleplus.eu. For any specific questions, contact Access Officer Florence Guillot; Email: access (at) embrc.eu
Partners
ASSEMBLE Plus Access Providers in the European Marine Biological Resource Centre (EMBRC-ERIC) are:
• EMBRC-Belgium (VLIZ, UGENT),
• EMBRC-France (Sorbonne Universités, CNRS),
• EMBRC-Greece (HCMR),
• EMBRC-Israel (HUJI),
• EMBRC-Italy (SZN, CNR),
• EMBRC-Norway (UiB),
• EMBRC-Portugal (CCMAR, IMAR, CIIMAR),
• EMBRC-Spain (UPV/EHU, UVIGO),
• EMBRC-UK (SAMS, USTAN, MBA, NERC-BAS, MSS),
ASSEMBLE Plus Access Providers not currently member of EMBRC-ERIC:
• Finland (UH),
• Germany (AWI, MPIMM),
• Ireland (NUIG),
• The Netherlands (NIOZ),
• Poland (IOPAN, UG-Gdansk),
• Slovenia (NIB),
• Sweden (UGOT – SLC).
Detailed information on the Access Providers is available on the ASSEMBLE Plus website at http://www.assembleplus.eu/
This distributed partnership provides access to diverse marine ecosystems and their biodiversity of the European coastal seas, the Red Sea (HUJI), the Caribbean (NIOZ), the Arctic (IOPAN) and the Antarctic (NERC-BAS).
Research Area
Research Infrastructure
Project Lifetime
48 months as of 1 October 2017
SZN Role
The SZN lead the Work Package “NA1 Improving Transnational Access (TA) provision”, coordinating the input from UPMC, UGOT, UPV/EHU, CCMAR, VLIZ, MSS.
The main objectives are:
• Establish a policy for regulating, granting and supporting TA;
• Set up single-access point for TA to the offered infrastructure;
• Test TA-pipelines through ASSEMBLE Plus and cognates in joint calls;
• Share best practices among platforms and services;
• Improve the efficiency of TA service provision.
SZN is involved as partner in three Joint Research Activities (JRAs).
JRA1 Genomics observatories
JRA3 Functional genomics
JRA4 Development of instrumentation
TA: In Italy, the SZN coordinates the transnational access to SZN in Naples and Ischia and to its Third Parties ISMAR-CNR in Venice http://www.ismar.cnr.it and IAMC-CNR in Messina http://www.iamc.cnr.it/index.php/contattaci/). All give access to Mediterranean pelagic and benthic hard- and soft bottom ecosystems.
SZN includes the main building in the Villa Comunale in Naples, the benthic ecology laboratory at Ischia Porto and the turtle research centre at Portici. Visitors have access to service platforms and research laboratories. SZN does not operate a guesthouse given ample supply of hotels and B&Bs nearby. SZN has extensive experience with collecting and maintaining model species and performing multi- disciplinary research on these organisms http://www.szn.it/index.php/en/research
Principal Investigator
Funding Institution
Université Sorbonne coordinates the project.
Contribution to SZN
€ 1.017.745,25 of which € 289.702,00 to the Third Parties
Dedicated website
 |
Presentazione del libro "Eco-Devo - Ambiente e Biologia dello sviluppo" Mercoledì 4 Settembre 2019, ore 17.00 Intervengono: Silvia Caianiello, Maurizio Casiraghi, Lorenzo Chiariotti |
 |
Un mare di plastica: come uscirne? Venerdì 24 maggio 2019, ore 17.00 Introduce: Domenico D’Alelio Intervengono: Mario Malinconico, Paolo Degiovanni, Alfonso Marino |
 |
Incontro con l'autore - La canzone del Guarracino Martedì 14 maggio 2019, ore 18.00 Ne parleranno: Chiara Arturo, Christiane Groeben, Eugenio Lucrezi e gli editori Lina Marigliano e Alberto D’Angelo Scena sonora con musiche originali di Tonino Taiuti |
 |
L’utilizzo della cinematografia nelle scienze Martedì 12 febbraio 2019, ore 16.30 Moderano: Anna Masecchia e Marcello Seregni Intervengono: Lorenzo Lorusso, Virgilio Tosi, Monica Zoppè Verrà presentato AA.VV., Osvaldo Polimanti e le origini della cinematografia scientifica, Carocci, Roma 2011, a cura di Lorenzo Lorusso, Virgilio Tosi, Giovanni Almadori |
 |
Internet e Democrazia Venerdì 11 gennaio 2019, ore 16.00 Intervengono: Guido Caldarelli, Rosanna De Rosa, Luciano Fasano
|