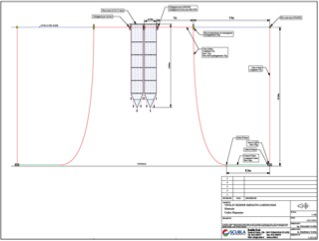
Among the park's oceanographic instruments, the SZN has a set of pelagic mesocosms built ad-hoc for running controlled in situ experiments in coastal waters. These mesocosms (6 structures) have a capacity of about 100 m3, with a depth of 15 meters. They are equipped with a pumping system allowing sampling at three depths, 0.2, 5 and 10 meters, as well as temperature and light sensors put at the same three depths.
These systems allow us to carry out experiments in the sea for a short period (<1 month) and areas protected from rough seas or strong waves that could destroy the installation.
Mesocosms are experimental tools that allow us to perform in situ studies on pelagic ecosystem, at intermediate scale between microcosms setup in laboratory and the complexity of the real world.
 Mesocosms are facilities that allow us to enclose the water mass present during the installation of the structures, and therefore keeping all the properties of the ecosystem. There is not exchange with outside, avoiding any influence from horizontal or vertical advection.
Mesocosms are facilities that allow us to enclose the water mass present during the installation of the structures, and therefore keeping all the properties of the ecosystem. There is not exchange with outside, avoiding any influence from horizontal or vertical advection.
The advantages of studies with such systems are:
- They allow to study the response (in time) of the ecosystem to induced environmental change.
- They allow to perform complex and optimal sampling designs for understanding the functioning of coastal pelagic ecosystems.
- They allow to investigate the ecosystem or part of its components in realistic environmental conditions.
- They allow to investigate almost all the food web at the same time.
- They allow the study of interactions in food webs.
- They allow the study of interactions between the different components and/or functional groups present in the ecosystem.
- They allow the study of the flow of matter in the ecosystem and then to parameterize it.
- They allow to perform studies with replicates.