Coastal Ecosystem Functioning in a changing Antarctic ocean (CEFA)
Environmental Monitoring in Relation to the Connection of the Campania Islands to the National Power Network. Torre Annunziata – Capri Leg
Hydraulic reclamation of Miseno lake and reopening, settlement and protection of the mouth of the Fusaro lake - Project "Environmental rehabilitation and improvement of the campi Flegrei lakes"
UV-Visible spectophotometer Agilent 8453
 |
The instrument measures the light absorption of mixtures or UV - visible standards in order to obtain the exact concentration of the compound of interest |
SHIMADZU RF-5301PC spectrofluorometer
 |
It is used for the quantitative and / or qualitative analysis of fluorescent substances. Taking advantage of the high sensitivity, it allows the quantitative determination of substances present in concentrations too low for spectrophotometric analyses |
HPLC Agilent 1100 series
 |
The HPLC is an analytical instrument utilized to separate and to purify the components of a sample mixture, to identify and to quantify each component |
Thermo Scientific FlashEA 1112 Elemental Analyzer
 |
The Thermo Scientific FlashEA 1112 analyzer delivers rapid and precise determinations of Nitrogen and Carbon on solids |
Flow Sys Systea Autoanalyzer
 |
It allows the simultaneous analysis of nutrients (nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, phosphate and silicate). Moreover , analyses of total and dissolved organic Nitrogen and Phosphorus can be carried out |
PhytoPam Walz
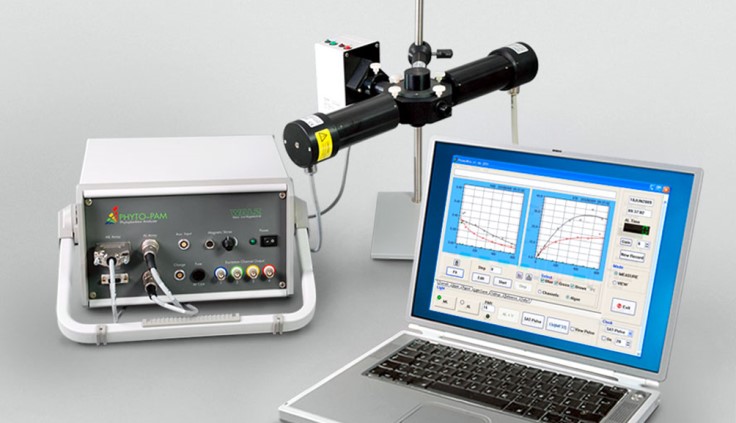 |
PHYTO-PAM can be used to assess the photosynthetic performance and light-adaptation status of different types of phytoplankton |
Remote Operating Vehicle - ROV POLLUX III
 |
The instrument is used for visual exploration of the seabed through a controlled cable edge which guides the underwater vehicle and can operate up to a maximum depth of 300m |
Independent Oceanographic Platform Remote Programmable and Operable- Wave Glider - SV3 074
 |
The instrument is an oceanographic platform with a self-motive, autonomous and programmable detection operable remotely. It is equipped with oceanographic and meteorological sensors |
VMP 250 (TurboVMP) Vertical Turbulence Profiler
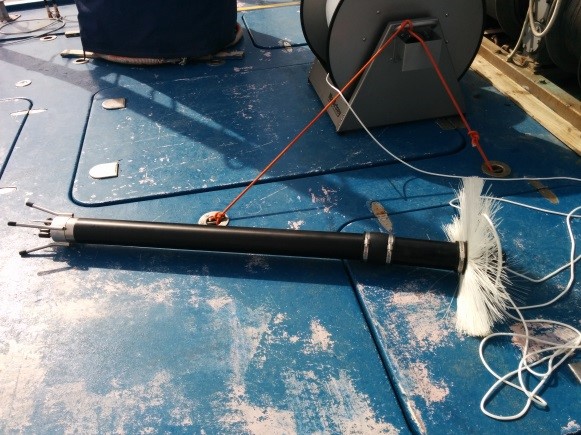 |
It is a versatile profiler for the measurement of micro-scale turbulence |
Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 – Agilent Technologies
|
 |
Applied Biosystems ViiA7 384 wells format - Life Technologies
|
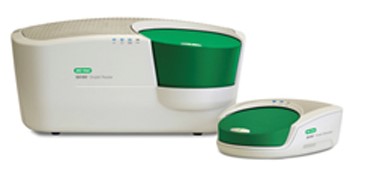 |
QX200 Droplet Digital PCR System. QX200 Droplet Reader (sx), QX200 Droplet Generator (dx) |
 |
Applied Biosystems 3730 DNA Analyzer 48 capillaries - Life Technologies |
 |
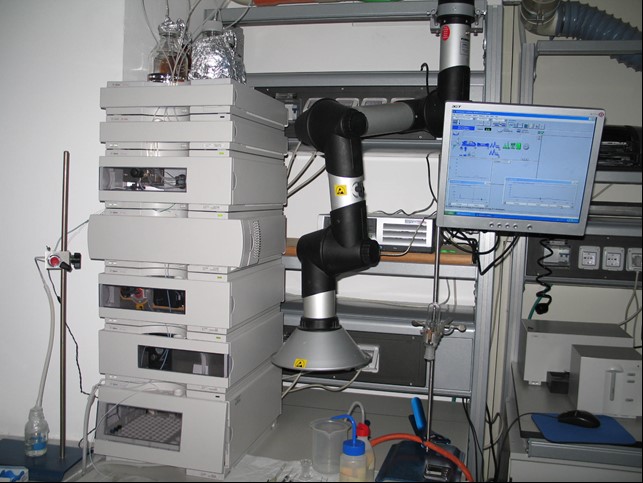
HTS platform FREEDOM EVO 200 - TECAN
|
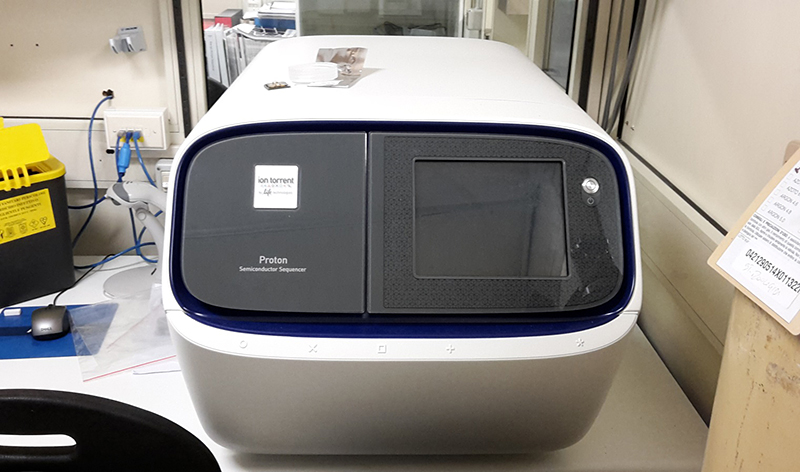 |
ION Proton semiconductor sequencer- Life Technologies
|
Analyses of environmental and biological variables |
|
 |
Data processing of the automatic profilers, chemical and instrumental analyses of the main environmental and biological variables |
Coastal monitoring of chemical, physical and biological parameters |
|
 |
Continuous monitoring system along the Gulf of Naples coast |
Coastal vessels management |
|
 |
The MEDA unit manages two coastal vessels (M/B Vettoria and M/B Hippocampus), used for environmental monitoring, research and teaching. Moreover, it provides support for their use |
Hydrographic surveys and sampling |
|
 |
Continuous acquisition by means of multi-parametric probes and/or profilers. Collection and pre-treatment on board of samples for the main chemical and biological analyses |
Material collection and scuba diving |
|
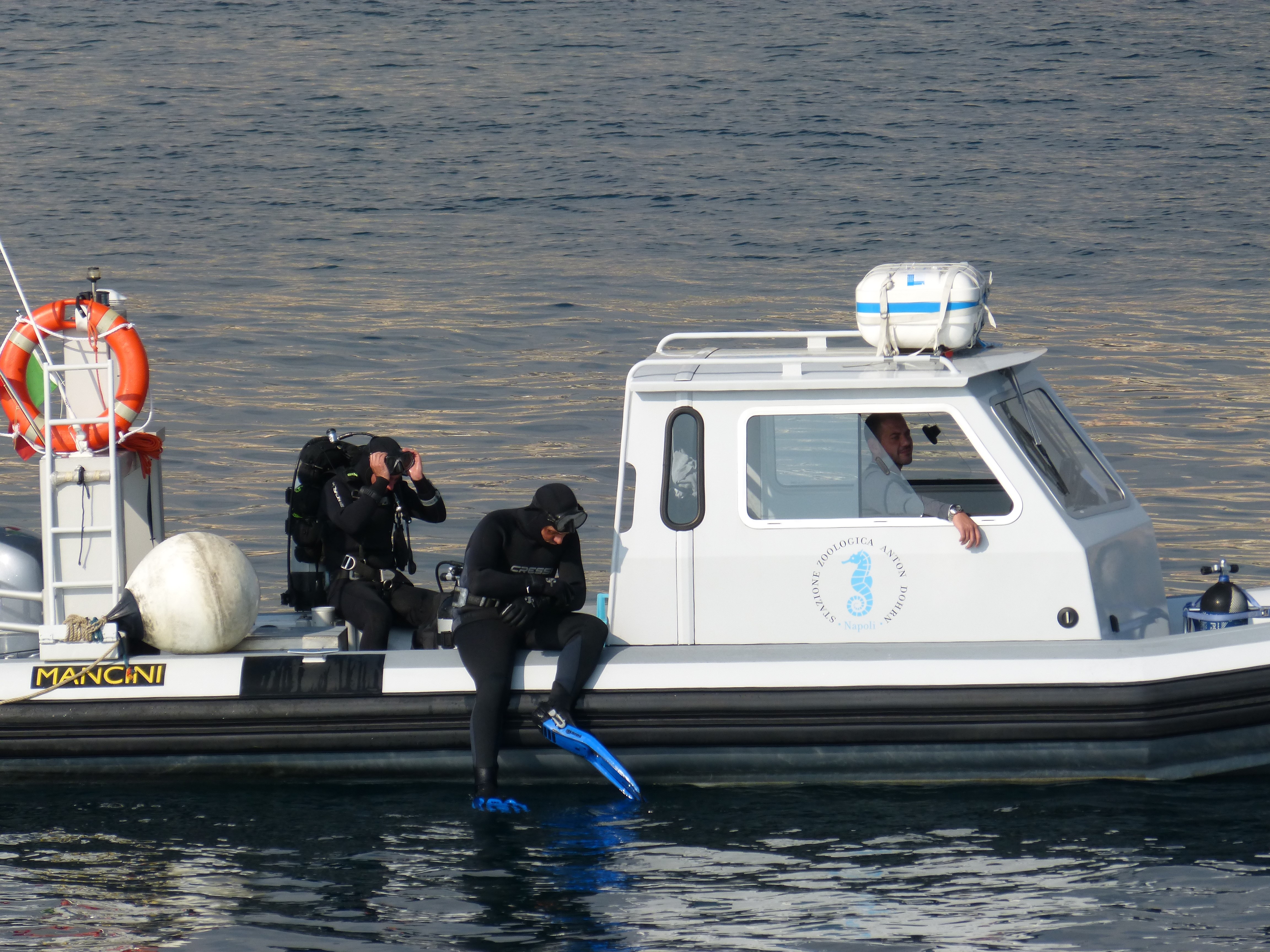 |
The unit deals with the collection of material to be used for both research and outreach activities Moreover, it carries out scuba diving activities |
Monitoring and environmental consulting |
|
 |
Sampling, environmental analysis, data elaboration and drafting of technical and scientific reports, in the context of different types of environmental monitoring commissioned by local and national institutions or private entities |
Basic Services for Molecular Biology
Preparation and distribution of media and plates for bacteriology, of media for animal cell culture, of several products and reagents for Molecular Biology and ISH, of competent cells for bacterial transformation etc. Provisioning of synthetic oligonucleotides.
Qualitative control of nucleic acids
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of nucleic acids and definition of the reference standard for the QC of the RNA samples by microfluidic chip.
Real Time qPCR
Real Time qPCR mainly used for analysis of gene expression. Support to users includes assistance with experimental design, running of samples, and if requested, initial data analysis.
Droplet Digital PCR (in progress)
The ddPCR allows to:
Detect small amounts of target DNA molecules, with high sensitivity.
Determine the change in the number of genomic copies with high accuracy.
Measure gene expression levels with high precision.
Quantify NGS libraries.
DNA Sequencing service
Automated DNA sequencing by capillary electrophoresis essential for the study of nucleic acids from plasmids, PCR fragments , phage , etc.
Genotyping service
Used for genetic population studies by analysis of::
- Microsatelliti (single-locus).
- Snips, (single-locus).
- AFLP, (multi-locus).
Automation and High Throughput Screening (HTS) projects
Realization in automation, by Robotics (liquid handler), of a high-throughput projects for those research activities that require, in the short term, the analysis of a large number of samples.
Next Generation Sequencing service (NGS) (in progress)
Next generation sequencing (NGS) using "ION Proton" (Life Technologies) can produce data for transcriptomic studies, metagenomics, gene expression analysis, and targeted Resequencing.