Towards an integrated observing system in the Gulf of Naples

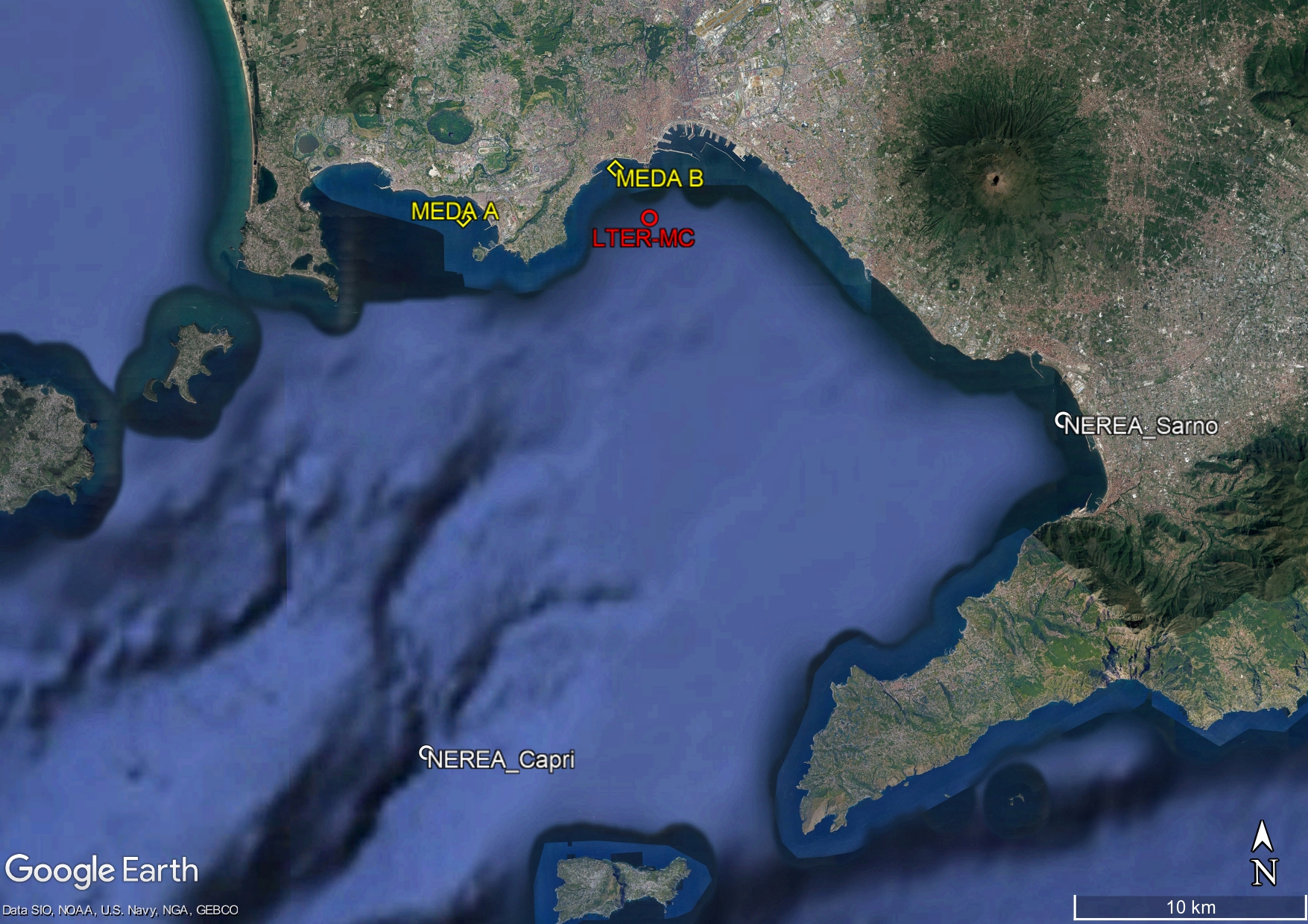
The Gulf of Naples (Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Western Mediterranean Sea) extends between 40°50’-40°32’N and 13°52’-14°28’E, with an area of 870 km2 and an average depth of 170 m. About 4 million people live along the coasts, which have been inhabited since the pre-Roman age. The Gulf is characterized by the contrast between highly polluted areas (Bagnoli-Coroglio, Eastern-Naples) and pristine sites identified as Marine Protected Areas (Punta Campanella, Regno di Nettuno).
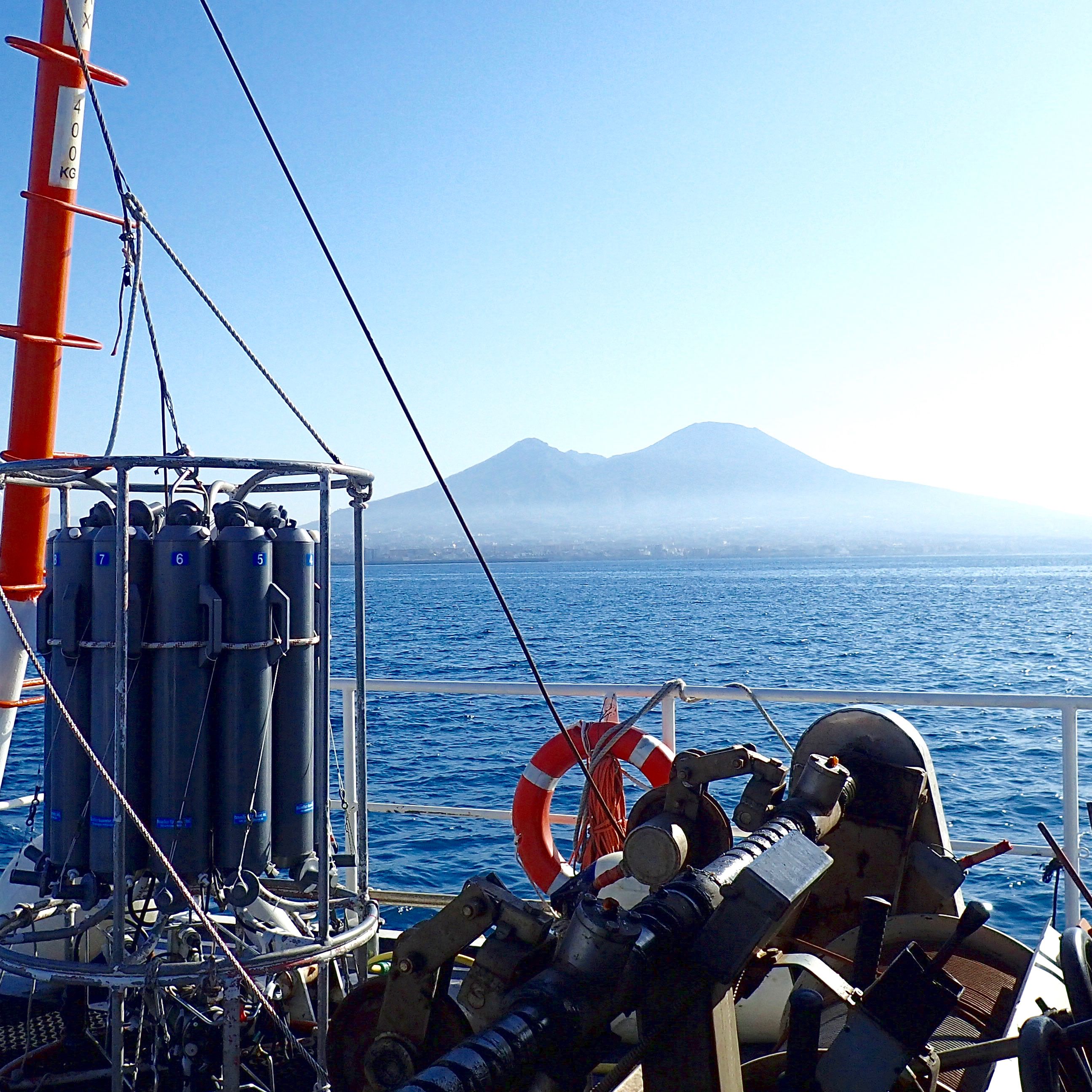
 The Research Program MareChiara was launched by SZN in 1984 with the aim of investigating the structure and functioning of planktonic communities of the Gulf of Naples in relation to the environmental variability and climate change. Since 2006, the station LTER-MareChiara (LTER-MC) is part of the national (LTER-Italy) and international networks of Long Term Ecological Research sites (I-LTER, E-LTER). LTER- MC is located 2 miles offshore the city of Naples, on the 75 m isobath, at the boundary between the coastal area, influenced by land runoff, and the offshore oligotrophic waters with characteristics of the southern Tyrrhenian Sea. In support to the observational activities, two MEDA-elastic buoys (MEDA A and MEDA B) were installed in 2016 at a short distance from the coast, one off the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn and the other off Bagnoli. The buoys are equipped with meteorological sensors, multiparametric profiling probes and ADCP current-meters. High-frequency data are transmitted in real time via a broadband Wi-Fi bridge and also via the GSM network. In 2022 LTER-MC and the «Gulf of Naples integrated pelagic observatory» has been nominated “Endorsed Decade Action” by the United Nations under the Marine Life 2030 program (https://oceandecade.org/actions/gulf-of-naples-integrated-pelagic-observatory/).
The Research Program MareChiara was launched by SZN in 1984 with the aim of investigating the structure and functioning of planktonic communities of the Gulf of Naples in relation to the environmental variability and climate change. Since 2006, the station LTER-MareChiara (LTER-MC) is part of the national (LTER-Italy) and international networks of Long Term Ecological Research sites (I-LTER, E-LTER). LTER- MC is located 2 miles offshore the city of Naples, on the 75 m isobath, at the boundary between the coastal area, influenced by land runoff, and the offshore oligotrophic waters with characteristics of the southern Tyrrhenian Sea. In support to the observational activities, two MEDA-elastic buoys (MEDA A and MEDA B) were installed in 2016 at a short distance from the coast, one off the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn and the other off Bagnoli. The buoys are equipped with meteorological sensors, multiparametric profiling probes and ADCP current-meters. High-frequency data are transmitted in real time via a broadband Wi-Fi bridge and also via the GSM network. In 2022 LTER-MC and the «Gulf of Naples integrated pelagic observatory» has been nominated “Endorsed Decade Action” by the United Nations under the Marine Life 2030 program (https://oceandecade.org/actions/gulf-of-naples-integrated-pelagic-observatory/).
Since March 2019 an augmented observatories established in the frame of ongoing monitoring programs, at Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) sites, and in two preferential sites at the mouth of the Sarno river (Nerea_Sarno) and on the Dohrn Canyon off Capri (Nerea_Capri). Sampling monthly involving the use of molecular methods to increase the taxonomic and functional detail of the biodiversity of the Gulf of Naples.
The  Observatory is called NEREA (Naples Ecological research Augmented observatory www-nerea observatory.org) and has received the endorsement of the United Nations as a project under the OBON program (Ocean Biomolecular Observing Network https:///www.oceandecade.org/actions/ocean-biomolecular-observing-network-obon/). NEREA also participates in the EMOBON initiative (European Marine Omics Biodiversity Observation Network https:///www.embrc.eu/emo-bon).
Observatory is called NEREA (Naples Ecological research Augmented observatory www-nerea observatory.org) and has received the endorsement of the United Nations as a project under the OBON program (Ocean Biomolecular Observing Network https:///www.oceandecade.org/actions/ocean-biomolecular-observing-network-obon/). NEREA also participates in the EMOBON initiative (European Marine Omics Biodiversity Observation Network https:///www.embrc.eu/emo-bon).